
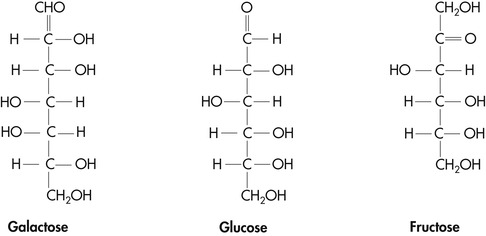
 A monosaccharide is defined as a polyhydroxy aldehyde (aldose) or a polyhydroxy ketone (ketose).Ĭarbohydrates are structurally represented in one of three ways:. The building blocks of all carbohydrates are monosaccharides, or simple sugars. They are organic compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups coming off the carbon chain that are organized as aldehydes or ketones.
A monosaccharide is defined as a polyhydroxy aldehyde (aldose) or a polyhydroxy ketone (ketose).Ĭarbohydrates are structurally represented in one of three ways:. The building blocks of all carbohydrates are monosaccharides, or simple sugars. They are organic compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups coming off the carbon chain that are organized as aldehydes or ketones. 
The empirical structure of carbohydrates is (CH2O)n.Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen make up the molecules of carbohydrates.Reduction of alcoholic beverages: Sodium borohydride, NaBH4, or catalytic hydrogenation (H2, Ni, EtOH/H2O) can reduce the C=O groups in open-chain carbohydrates to alcohols.”Alditols” is the name given to the products.D-glucose is oxidized to D-gluconic acid in Benedict’s test, making glucose a reducing sugar. Oxidation: If the carbonyl groups in monosaccharides oxidize to form carboxylic acids, they are referred to as reducing sugars.When Benedict’s reagent solution and reducing sugars are heated together, they turn an orange-red/brick red colour.
 Benedict’s challenge: When reducing sugars are heated in the presence of an alkali, they are converted to enediols, which are powerful reducing species. The two sugars are D-glucose and L-glucose. In terms of the penultimate carbon atom, there are two isomers of glucose. Sugars react with an excess of phenylhydrazine to form osazone, which is a carbohydrate derivative. Anomerism is the spatial configuration of the first carbon atom in aldoses and the second carbon atom in ketoses with respect to the first carbon atom. Diastereoisomers are configurational changes in glucose involving C2, C3, or C4. Optical Activity – The rotation of plane-polarized light that produces (+) and (-) glucose. These are the two sugars: D-glucose and L-glucose. When it comes to the penultimate carbon atom, there are two isomers of glucose. Stereoisomerism refers to compounds that have the same structural formula but differ in their spatial configuration. Enzymes in your digestive tract break down long glucose chains into smaller sugars that your cells can use when you eat French fries, potato chips, or a baked potato with all the fixings.Carbohydrates are biological molecules that are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of one carbon atom to one water molecule. The majority of carbohydrate is in the form of starch, which is made up of long chains of linked glucose molecules and is used as a storage fuel.
Benedict’s challenge: When reducing sugars are heated in the presence of an alkali, they are converted to enediols, which are powerful reducing species. The two sugars are D-glucose and L-glucose. In terms of the penultimate carbon atom, there are two isomers of glucose. Sugars react with an excess of phenylhydrazine to form osazone, which is a carbohydrate derivative. Anomerism is the spatial configuration of the first carbon atom in aldoses and the second carbon atom in ketoses with respect to the first carbon atom. Diastereoisomers are configurational changes in glucose involving C2, C3, or C4. Optical Activity – The rotation of plane-polarized light that produces (+) and (-) glucose. These are the two sugars: D-glucose and L-glucose. When it comes to the penultimate carbon atom, there are two isomers of glucose. Stereoisomerism refers to compounds that have the same structural formula but differ in their spatial configuration. Enzymes in your digestive tract break down long glucose chains into smaller sugars that your cells can use when you eat French fries, potato chips, or a baked potato with all the fixings.Carbohydrates are biological molecules that are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of one carbon atom to one water molecule. The majority of carbohydrate is in the form of starch, which is made up of long chains of linked glucose molecules and is used as a storage fuel.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
